
September 2024
Getting More Common:
The Growing Reach of Gene Therapy
- Although gene therapy has historically focused on rare diseases, recent years have seen increased development aimed at expanding its use to potentially treat common diseases.
- Common diseases are more amenable to gene addition approaches, often targeting broader mechanisms with wider applicability, as opposed to focusing solely on disease-causing mutations, which is standard for gene editing and replacement approaches.
- It's critical to consider the implications of expanding gene therapy to common diseases, including clinical and commercial factors such as adoption logistics, gene therapy value proposition, and pricing.
Increased comfort among key stakeholders, advances in gene delivery, and identification of novel genetic targets are key drivers for expansion of gene therapy into common diseases*
Key Factors Driving Development of Gene Therapy in Common Diseases
Clinical and commercial stakeholders’ comfort with GTx continues to grow, alongside a steady rise in FDA/EMA approved gene targeted agents and increasing utilization.
Novel viral/non-viral delivery methods evade issues with immunogenicity, which is a key challenge with current vectors that excludes ~50% of the population and does not allow redosing.
An increasing body of genetics data and functional genomics allows for a deeper understanding of key genetic interactions with therapeutic potential beyond those causing monogenic diseases.
*Any disease that affects >200,000 individuals in the U.S. is classified as a common disease.
Source: Bluestar Analysis
The majority of GTxs for common diseases are in early-/mid- stage development and focus on ophthalmology and cardiology
Clinical Development of Gene Therapies for Common Diseases
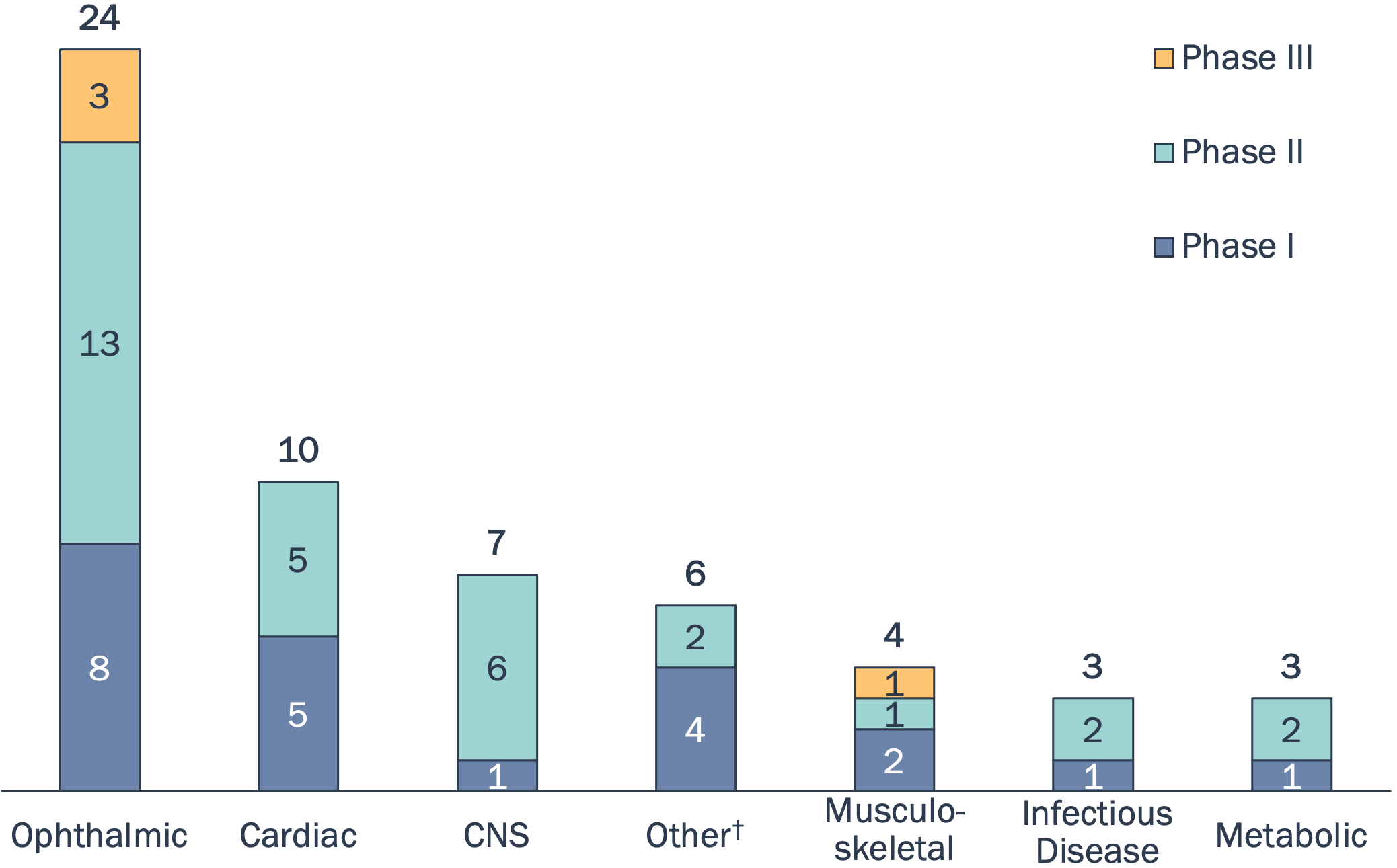
† Other includes otolaryngology and dermatology. Source: PharmaProjects
The majority of assets are in Ph I/II clinical trials with only 4 assets in Phase III development.
15 assets have been granted fast-track designation by the FDA.
Ophthalmology is a key area of focus (e.g., AMD, glaucoma, AMD, dry eye) followed by cardiac diseases (e.g., heart failure).
Higher selectivity of common delivery vectors towards cardiac tissue and ease of access to the eye likely influence current TAs in focus.
Common diseases are most amenable to gene addition compared to editing/replacement methods, which have stronger applicability in rare, monogenic diseases
GTx Trends by Approach in Common Diseases
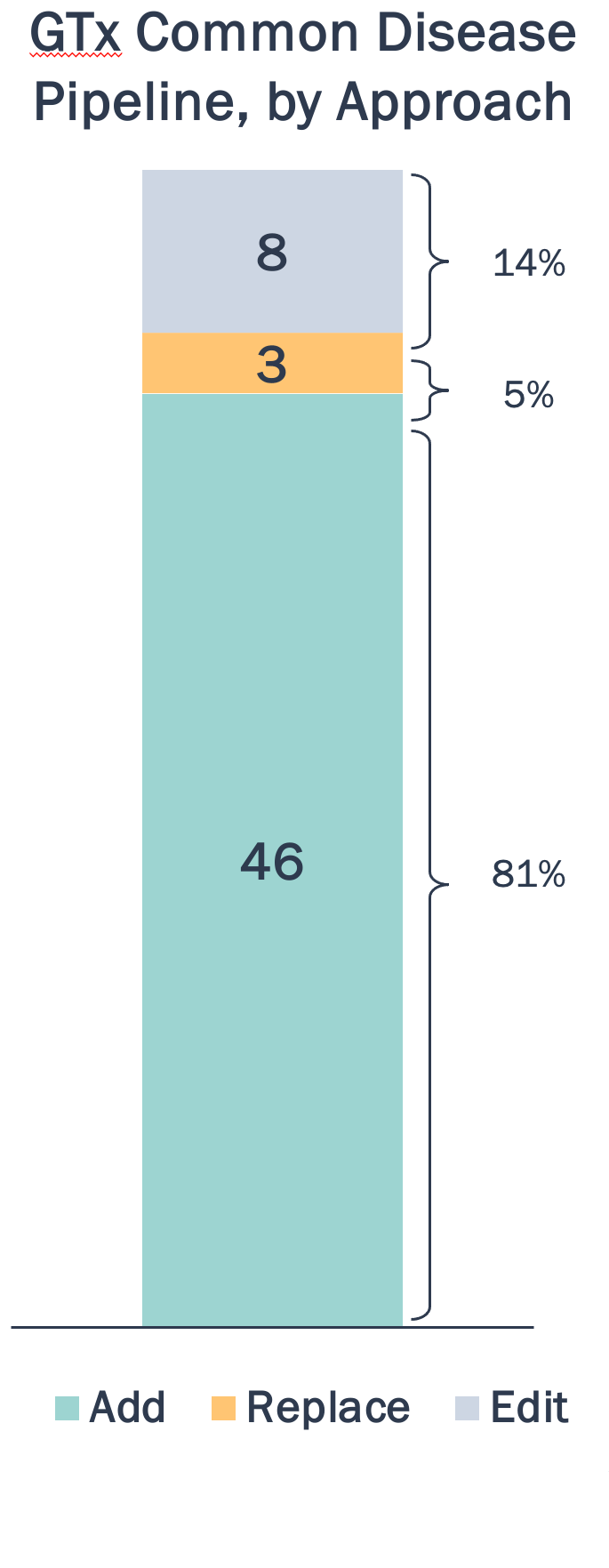
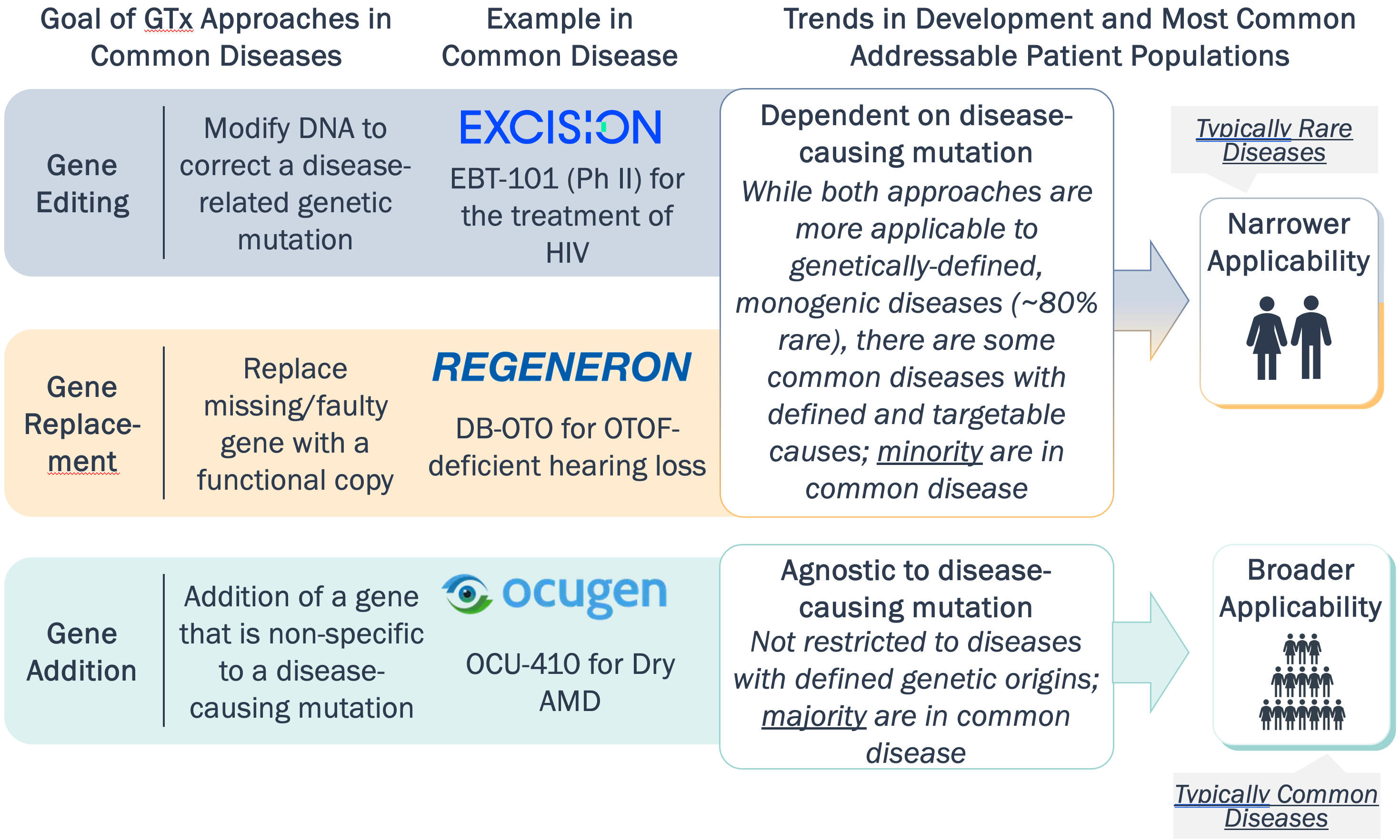
Gene addition approaches often utilize targets, like SERCA2a in HF, with potential to slow disease progression and mitigate symptom development without targeting causal mutations
Potential Use of GTx in Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM) & Heart Failure (HF)
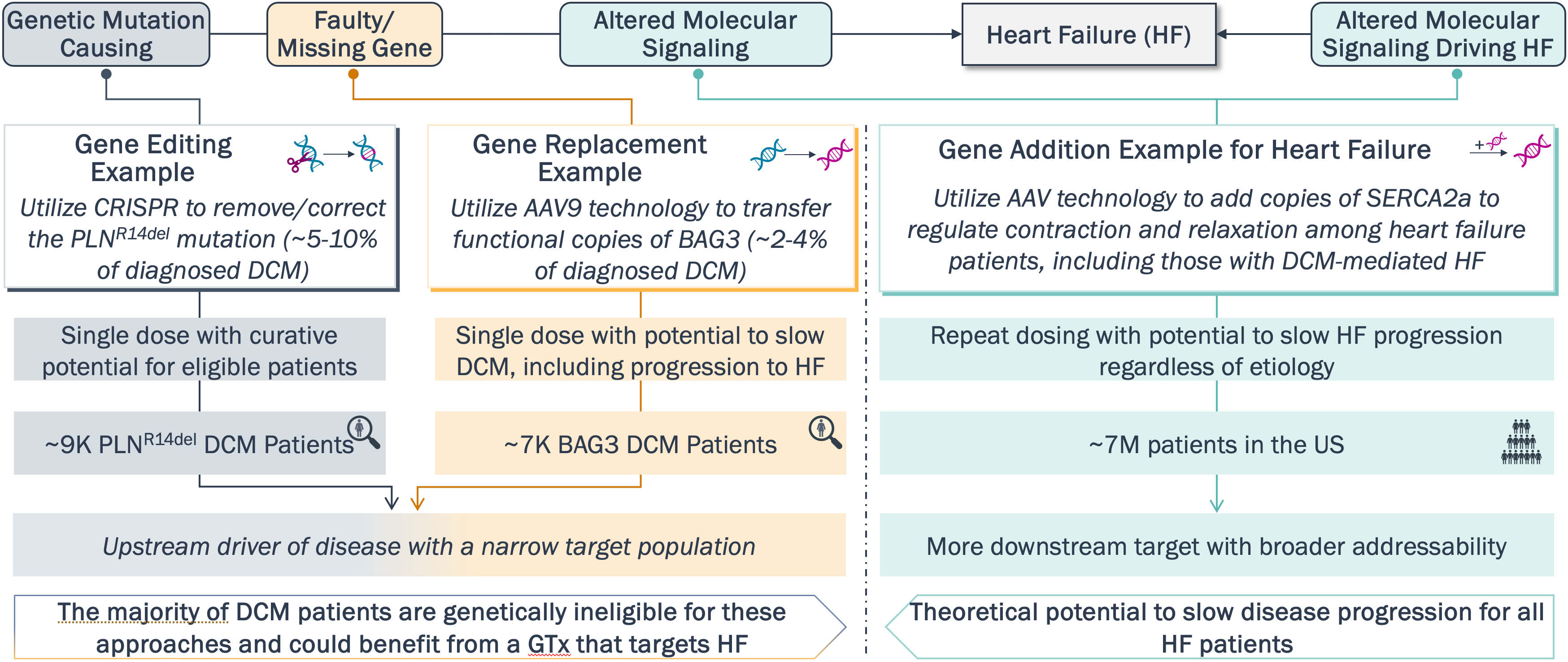
Potential expansion of GTx therapy into the common disease space further highlights the importance of monitoring the rapidly evolving landscape
Future Considerations
Historical Trends
Among Approved Gene Therapies
Adoption
- High receptivity towards GTx among key stakeholders (i.e., physicians, patients, caregivers, advocacy groups)
- Due to the novelty and complexity associated with GTx administration, only select centers are equipped to deliver approved GTxs, thereby limiting capacity
GTx Value Proposition
- Provide treatment for high unmet need patient populations (e.g., rare, high disease burden)
- Offer significant clinical benefit, including curative potential and typically one time administration
Pricing
- Drug prices for approved GTxs are largely driven by value proposition (e.g., curative potential, disease modifying) and small patient populations
- Particular emphasis on HEOR reducing long-term costs to the healthcare system
Key Considerations for Understanding the Broader Implications of GTx Use in Common Diseases
How does potentially lower efficacy affect market receptivity?
What actions will be necessary for GTx administration in a broader set of centers?
How does repeat dosing for gene addition approaches compare to other chronic treatments?
How will advancements to vector technology impact the potential for GTx in common diseases?
How will value proposition for GTxs in common diseases be viewed by payers?
How will payers influence GTx use in common diseases that may have more treatment options?